Performances and behavior of a water-soluble and pH-sensitive polycarboxybetaine used for metal ion recovery
Performances and behavior of a water-soluble and pH-sensitive polycarboxybetaine used for metal ion recovery
Materials Today Communications 20, 100575, 2019
Mouton, J., Kirkelund, G.M., Hassen, Y., Chastagnol, S., Van den Berghe, H., Coudane, J., Turmine, M
ABSTRACT
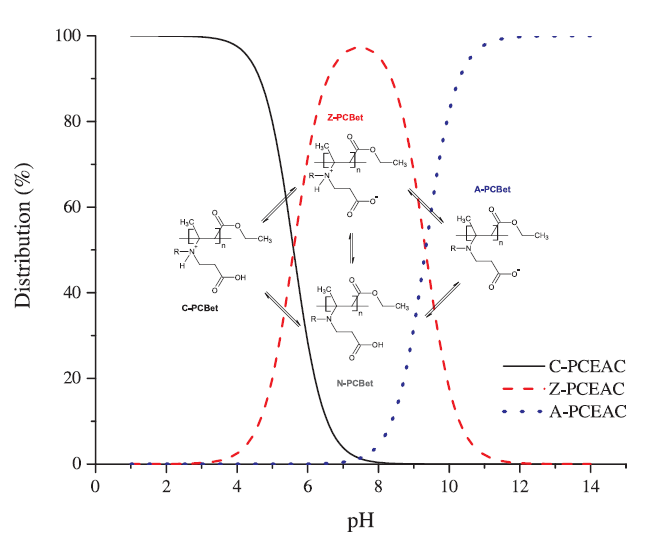
Zwiterionic functional groups give polycarboxybetaines a great ability to chelate copper and their use for metal ions recovery was suggested in previous studies. The use of a water-soluble and pH-sensitive polymer (polycarboxy-ethyl-3-aminocrotonate – PCEAC) was investigated for the removal of copper from aqueous solution. The equilibrium adsorption level was determined as a function of temperature, pH and initial adsorbate concentration. The good fit to the Langmuir model offered various information about copper uptake mechanisms. The maximal adsorption capacities were found to reach 253 ± 11 mg of copper per g of PCEAC at pH=6. The thermodynamic parameters such as free energy, enthalpy and entropy changes for the adsorption of copper were computed to predict the nature of adsorption process. The removal of copper was varying from 2% to 97% depending on pH and initial copper concentration. A particular behavior of PCEAC at pH=4 is discussed and explained by viscosity measurements as a particular conformation of the polymer. The effect of cadmium on copper adsorption was also tested. Some co-adsorption phenomena were observed at low cadmium concentrations ([Cd]/[Cu]≤1), while copper desorption in favor of cadmium adsorption were quantified at higher cadmium concentrations ([Cd]/[Cu]>1).


