MRI-Visible Poly(ε-caprolactone) with Controlled Contrast Agent Ratios for Enhanced Visualization in Temporary Imaging Applications.
MRI-Visible Poly(ε-caprolactone) with Controlled Contrast Agent Ratios for Enhanced Visualization in Temporary Imaging Applications.
Biomacromolecules 14, 3626–3634 (2013).
El Habnouni, S., Nottelet, B., Darcos, V., Porsio, B., Lemaire, L., Franconi, F., Garric, X. & Coudane, J.

ABSTRACT
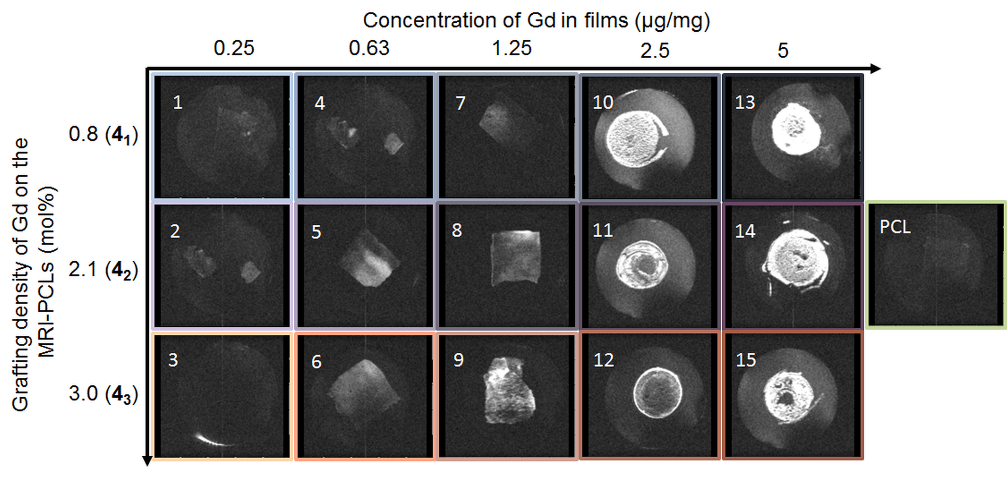
Hydrophobic macromolecular contrast agents (MMCAs) are highly desirable to provide safe and efficient magnetic resonance (MR) visibility to implantable medical devices. In this study, we report on the synthesis and evaluation of novel biodegradable poly(-caprolactone)-based MMCAs. Poly(α-propargyl-ε-caprolactone-co-ε-caprolactone)s containing 2, 5 and 10 mol% of propargyl groups have been prepared by ring opening copolymerization of -caprolactone and the corresponding propargylated lactone. In parallel, a di-azido derivative of the clinically used diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) / Gd3+ complex has been synthesized. Finally, MRI-visible poly(-caprolactone)s (PCLs) were obtained by the efficient click ligation of these compounds via a CuI-catalyzed [3+2] cycloaddition. ICP-MS analyses confirmed the efficient coupling of the complex on the PCL backbone with the MRI-visible PCLs containing 1.0, 2.6 and 3.6 wt% of Gd3+. The influence of the Gd3+ grafting density on the T1 relaxation times and on the MRI-visibility of the novel biodegradable MMCAs was evaluated. Finally, their stability and cytocompatibility were assessed with regard to their potential as innovative MRI-visible biomaterials for biomedical applications.


